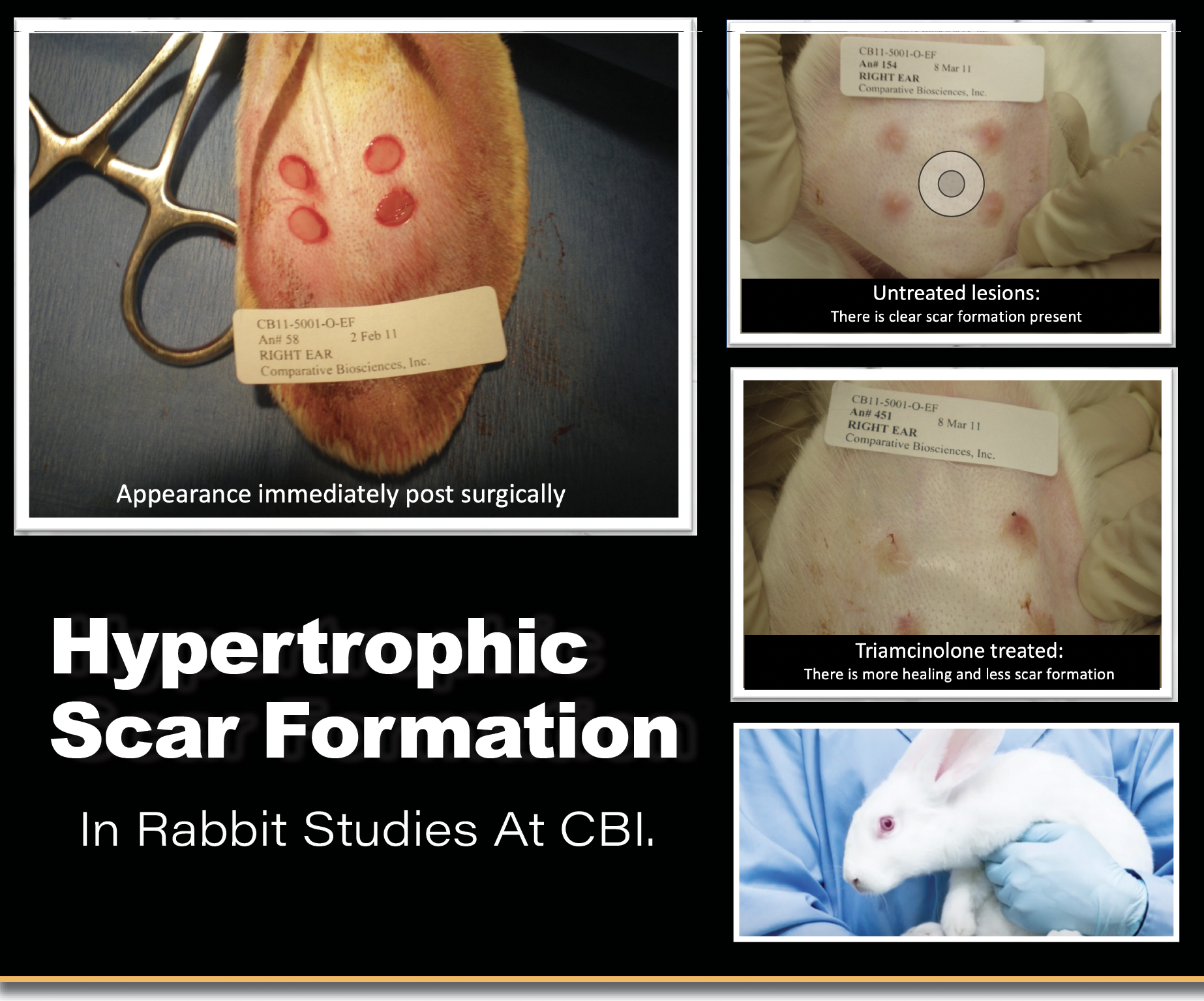
Four hypertrophic scars on the ventral side of a rabbit’s ear 4 weeks’ post-wound.
Hypertrophic Scar Formation in Rabbits
At CBI, an example of a standard Hypertrophic Scar Formation study, we first create a circular lesion with removal of the perichondrium elicits a proliferative fibrosis resulting in scar formation on the rabbit ear.
• This lesion can be measured and effects of test article determined
• Typical study setup:
• 6 weeks with dosing at day of wound formation
• After formation of scar (~3 weeks) with 3-4 weeks treatment
• With 2-3x weekly assessments and followed by histopathology for each
• Test article may be applied topically or intralesion injection
• Vehicle and test article applied to lesions
About Hypertrophic Scar Formation Studies
At CBI, we have a bold vision – Hypertrophic scars are benign and not harmful to a person’s general health. They do not develop into skin cancer. A hypertrophic scar will often regress completely between 6 months and 3 years after it first appears.
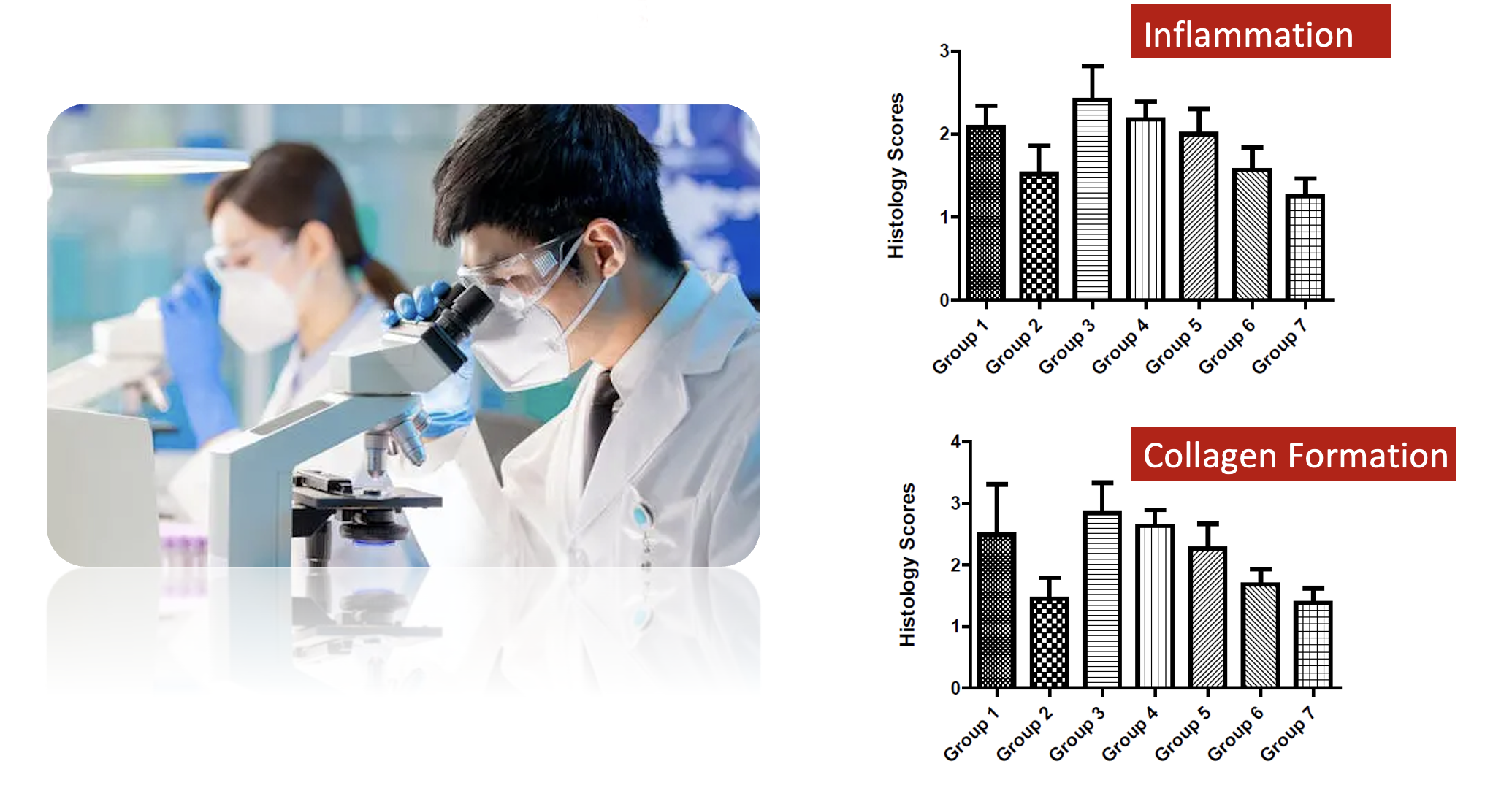
About Histopathologic Scores
Histopathologic scoring is a tool by which semi-quantitative data can be obtained from tissues. Initially, a thorough understanding of the experimental design, study objectives and methods are required to allow the pathologist to appropriately examine tissues and develop lesion scoring approaches.
Contact Comparative Biosciences, Inc. to discuss a scientific study program for all Studies and Services.
Comparative Biosciences, Inc. · Phone: 408.738.9260
– CUSTOM HYPERTROPHIC SCAR STUDIES UPON REQUEST –


